What is Therapeutic Cloning?
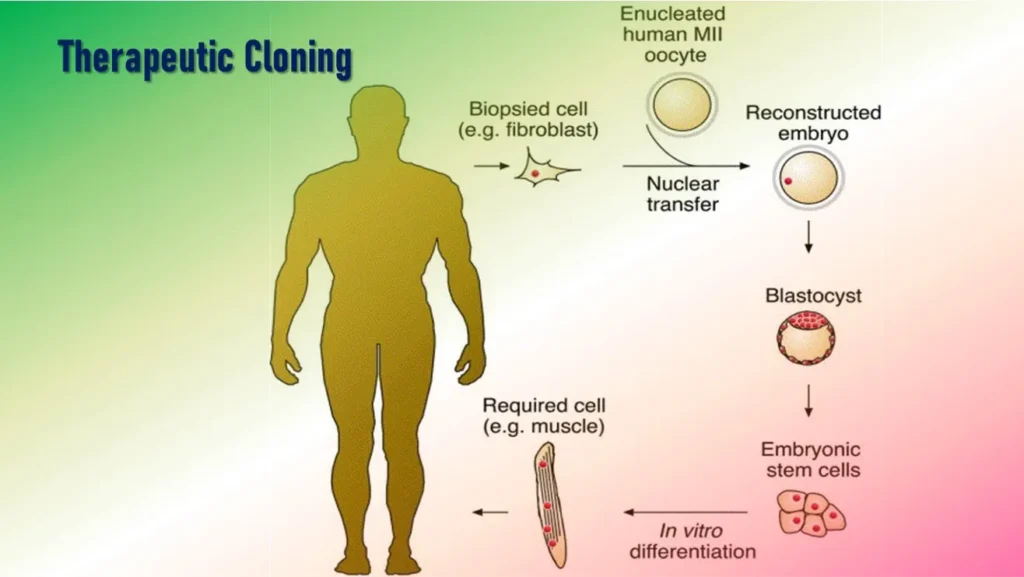
Therapeutic cloning is a technique to produce clonal stem cells. In this method, the transfer of nuclear material isolated from a somatic cell is carried out into an enucleated oocyte. This produces a clonal cell from where embryonic cell lines can be produced with the same genome as the nuclear donor.
These embryonic cells are harvested and used for stem cell based therapies. While the goal of reproductive cloning is the creation of a person, the purpose of therapeutic cloning is to generate patient-specific cell lines isolated from an embryo not intended for transfer in utero.
Therapeutic cloning offers great promises for regenerative and reproductive medicine, and in gene therapy, as a vector for gene-delivery.
Procedure of Therapeutic Cloning
- Nucleus is extracted from a sick person.
- The Nucleus is then inserted into an enucleated donor egg.
- The egg then divides like a typical fertilized egg and forms an embryo.
- Stem cells are removed from the embryo.
- Any kind of tissue or organ can be grown from these stem cells to treat various ailments and diseases.
Benefits (Advantages)
- A major benefit of therapeutic cloning is that the cells removed are pluripotent. Pluripotent cells can give rise to all cells in the body.
- This means that pluripotent cells can potentially treat diseases in any body organ or tissue by replacing damaged and dysfunctional cells.
- Another advantage is that the risk of immunological rejection is alleviated because the patient’s own genetic material is used.
- In addition, the procedure would allow scientists to create stem cell therapies that are patient specific and perfectly matched for the patient’s medical condition.
- Some of the diseases that could benefit from stem cell transplants are:
- Parkinson’s disease – replacing destroyed brain cells with healthy ones.
- Type I diabetes – providing viable functioning stem cells for the pancreas.
- Retinal diseases – transplanting stem cells to replace those in the retina that have been damaged by disease.
Potential Drawbacks (Disadvantages)
- Some experts are concerned about the striking similarities between stem cells and cancer cells.
- Both cell types have the ability to proliferate indefinitely and some studies show that after 60 cycles of cell division, stem cells can accumulate mutations that could lead to cancer.
- Therefore, the relationship between stem cells and cancer cells needs to be more clearly understood if stem cells are to be used to treat human disease.
Also Read:
What is Gene Editing and CRISPR with Working Mechanism
What are Stem Cells and its types with some Applications