What is a Stem Cell? A stem cell is a cell that is capable of extensive proliferation, creating more stem cells (self-renewal) as well as more differentiated cellular progeny.
They are, in effect, a population of embryonic cells, continuously producing cells that can undergo further development within an adult organism.
Development of the cells derived from the stem cells gives rise to the differentiated cell types.
The stem cells possess two fundamental characteristics:
- Self-renewal – the ability to go through numerous cycles of cell division while maintaining the undifferentiated state.
- Potency – the capacity to differentiate into specialized cell types.
Main Potency Types of Stem Cells
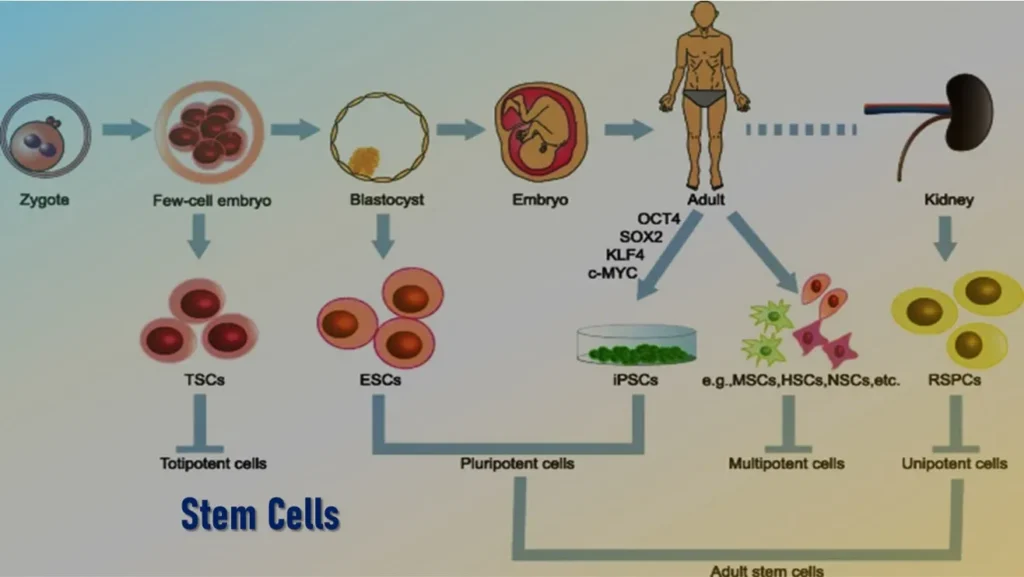
The stem cell types are known on the basis of their potency. Potency means the differentiation potential (the potential to differentiate into different cell types) of the stem cell. The following major types of stem cells are described:
Totipotent stem cells can differentiate into embryonic and extraembryonic cell types. Such cells can construct a complete, viable, organism. Such cells are mostly zygotic, produced from the fusion of an egg and sperm cell. Cells produced by the first few divisions of the fertilized egg are also totipotent.
Pluripotent stem cells are the descendants of totipotent cells and can differentiate into several unrelated types of cells.
Multipotent stem cells can differentiate into a number of cells, but only those of a closely related family of cells.
Oligopotent stem cells can differentiate into only a few cells, such as lymphoid or myeloid stem cells.
Unipotent cells can produce only one cell type, their own, but have the property of selfrenewal which distinguishes them from non-stem cells (e.g. muscle stem cells).
Occurrence of the Stem Cells
Stem cells are found in the embryo as well as in the adult body. The important sources of stem cells are as follows:
- Embryo: Embryonic stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst. They are pluripotent.
- Foetus: Foetal stem cells are mainly derived from germ cells derived from spontaneously aborted foetuses. Pluripotent stem cells are also found in the foetal brain.
- Adult Body: Stem cells can also be found in small numbers in various tissues in the adult body including brain and muscle tissues.
- Other Sources: Stem cells can also be obtained from other sources, for example, the umbilical cord of a newborn baby is a source of blood stem cells.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPS cells)
Induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells are a new type of pluripotent cells that are created by inducing the specialized cells to express genes that are normally present in embryonic stem cells and that control cell functions.
Embryonic stem cells and iPS cells share many characteristics, including the ability to become the cells of all organs and tissues, but they are not identical.
iPS cells are a powerful method for creating patient- and disease-specific cell lines for research. These are not adult stem cells, but rather reprogrammed cells with pluripotent capabilities.
iPS cells are useful tools for drug development and modeling of diseases, and scientists hope to use them in transplantation medicine.
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2012 was awarded jointly to John B. Gurdon and Shinya Yamanaka for the discovery that mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent stem cells.
Application of Stem Cells
Treatment of Brain Diseases
Stem cells can treat diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s. These can help to replenish the damaged brain cells.
Increase Understanding of How Diseases Occur
By watching stem cells mature into cells in bones, heart muscle, nerves, and other organs and tissue, researchers may better understand how diseases and conditions develop.
Test New Drugs for Safety and Effectiveness
Before using investigational drugs in people, researchers can use some types of stem cells to test the drugs for safety and quality.
This type of testing will most likely first have a direct impact on drug development for cardiac toxicity testing.
Tissue Regeneration
The stem cells can be used to grow a specific type of tissue or organ. This can be helpful in kidney and liver transplants.
The doctors have already used the stem cells from beneath the epidermis to develop skin tissue that can repair severe burns or other injuries by tissue grafting.
Blood Disease Treatment
The adult hematopoietic stem cells are used to treat cancers, sickle cell anemia, and other immunodeficiency diseases. These stem cells can be used to produce red blood cells and white blood cells in the body.
Also Read:
What is Gene Editing and CRISPR with Working Mechanism
What is Gene Therapy and Mitochondrial Disease?