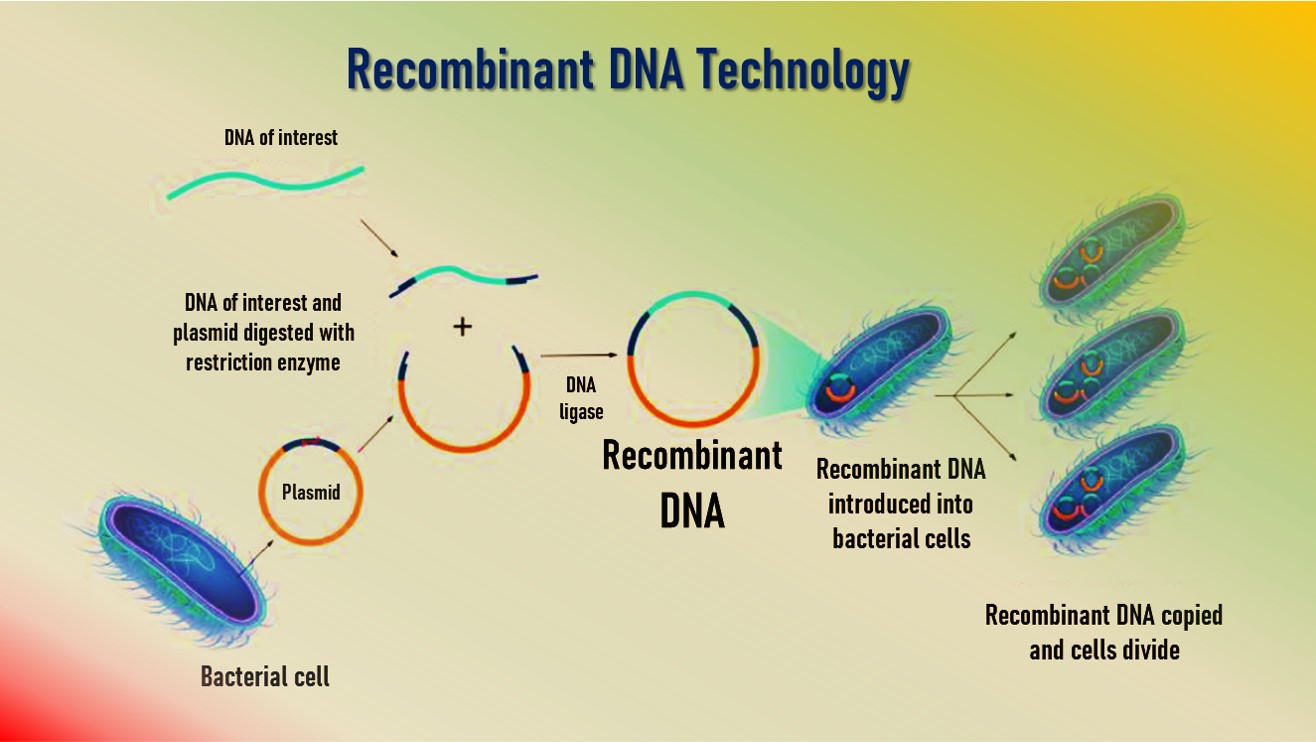
Introduction to rDNA Technology
- Recombinant DNA is an artificially made DNA strand that is formed by the combination of two or more gene sequences.
- rDNA technology involves using enzymes and various laboratory techniques to manipulate and isolate DNA segments of interest.
- The method can be used to combine (or splice) DNA from different species or to create genes with new functions.
- rDNA is possible because the DNA of all organisms share the same chemical structure but different nucleotide sequences within the overall identical structure.
- In 1973, Stanley N. Cohen and Herbert W. Boyer became the first to insert recombined genes into bacterial cells.
Tools of rDNA Technology
The key tools of Recombinant DNA Technology are restriction enzymes, polymerase enzymes, ligases, vectors and the host organism.
Applications of Recombinant DNA Technology
Medicine: genetic engineering has been used to mass-produce insulin, human growth hormones, follistim (for treating infertility), human albumin, monoclonal antibodies, antihemophilic factors, vaccines, and many other drugs.
Research: organisms are genetically engineered to discover the functions of certain genes.
Industrial applications: include transforming microorganisms such as bacteria or yeast. Mass quantities of the protein can be produced by growing the transformed organism in bioreactors using fermentation, then purifying the protein.
Agriculture: Genetic engineering is also used in agriculture to create genetically-modified crops or genetically-modified organisms. Crops containing genes which will enable them to withstand biotic and abiotic stresses have been developed. Crops with a number of desirable traits have also been developed such as Golden Rice, FlavrSavr Tomato etc.
Environment: Organisms have been known to help in the biodegradation of waste materials. However, there are some materials like plastics which cannot be degraded by them. To help such causes, genetic research has produced modified microorganisms which not only have the capability of doing this but are also more efficient due to the speedy process. They are used in situations which may cause severe damage to the planet earth like oil spills.
Also Read:
Artificial Satellites: Types, Working process and Applications
Applications of Nanomaterials in Medical and Healthcare industries
What is the definition of recombinant DNA technology?
Recombinant DNA is an artificially made DNA strand that is formed by the combination of two or more gene sequences. rDNA technology involves using enzymes and various laboratory techniques to manipulate and isolate DNA segments of interest.
The method can be used to combine (or splice) DNA from different species or to create genes with new functions. rDNA is possible because the DNA of all organisms share the same chemical structure but different nucleotide sequences within the overall identical structure. In 1973, Stanley N. Cohen and Herbert W. Boyer became the first to insert recombined genes into bacterial cells.
What are examples of recombinant DNA?
rDNA techniques, bacteria can synthesize human insulin, human growth hormone, alpha interferon, hepatitis B vaccine, and many other medically useful substances.










5 thoughts on “What is Recombinant DNA Technology ? Applications of rDNA Technology”