What is Satellite Launch Vehicles?
A Satellite launch vehicle is typically a rocket-powered vehicle designed to carry a payload i.e. satellites from Earth’s surface or lower atmosphere to outer space.
What are Launch Vehicles?
Launch vehicles or launch systems, as the names imply, are used to carry spacecraft from the surface of the Earth into space.
Most launch vehicles operate from a launch pad, supported by a launch control centre and systems such as vehicle assembly and fuelling.
They are classified by their orbital payload capacity, ranging from small, medium, heavy to super-heavy lift.
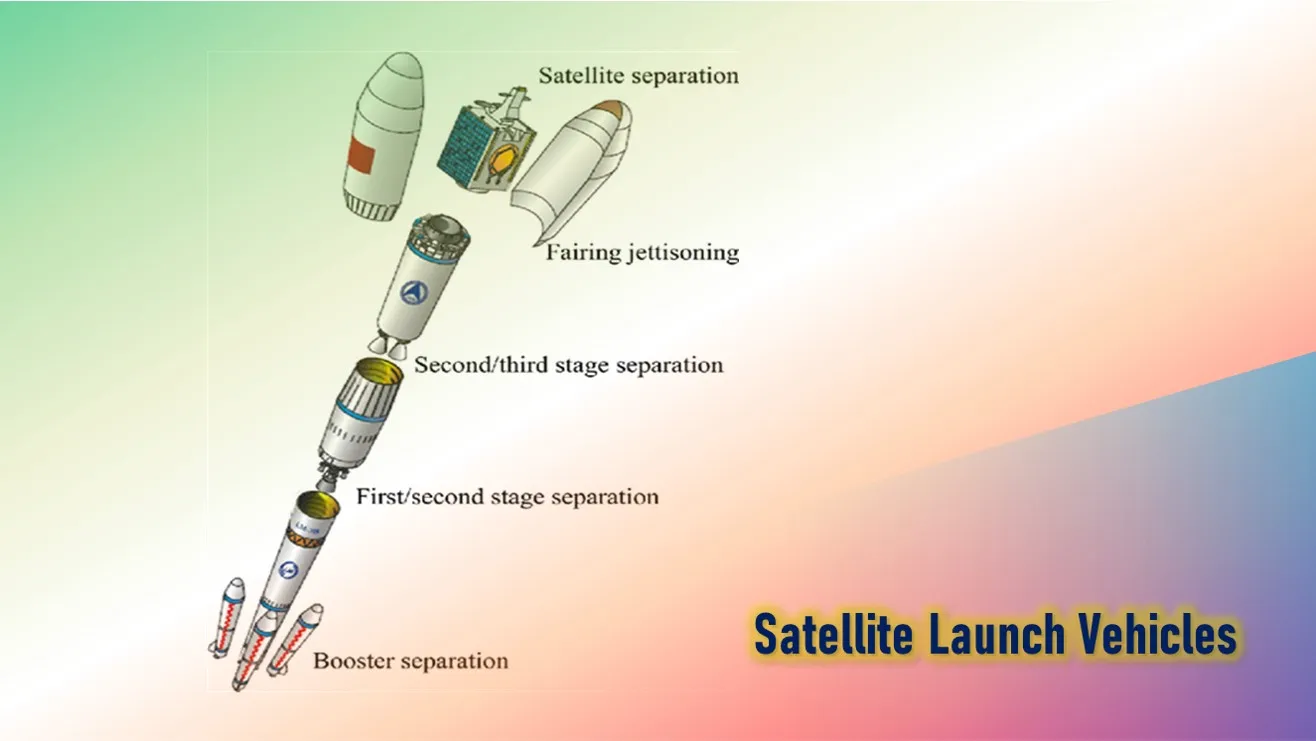
Launching of Satellite
The process of placing the satellite in a proper orbit is known as the launching process.
A launch vehicle is a good illustration of Newton’s third law of motion, i.e., “for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.”
In the case of a launch vehicle,
- “Action” is the flow out the rear of the vehicle of exhaust gases produced by the combustion of the vehicle’s fuel in its rocket engine, and
- “Reaction” is the pressure, called thrust, applied to the internal structure of the launch vehicle that pushes it in the direction opposite to the exhaust flow.
The launch of a spacecraft comprises a period of powered flight during which the vehicle rises above Earth’s atmosphere and accelerates at least to orbital velocity.
Powered flight ends when the rocket’s last stage burns out, and the spacecraft separates and continues in freefall.
Types of Satellite Launch Vehicle
The launch vehicles are basically multi-stage rockets and thus are mainly classified as:
Expendable Launch Vehicles (ELV)
An expendable launch vehicle is a single-use launch vehicle usually used to launch a payload into space. Most satellites are launched into orbit using expendable launchers.
Expendable launch vehicles typically consist of stages which are discarded one by one, in order not to have to carry and accelerate parts that are no longer needed.
The ELV contains three stages. First and second stages of ELV raise the satellite to about 50 miles and 100 miles. Third stage of ELV places the satellite in transfer orbit.
Once the satellite reaches the transfer orbit then the task of the launch vehicle will get completed and the various parts will get destroyed by themselves generally by falling to the earth.
Reusable Launch Vehicles (RLV)
This category of launch vehicles offers reusability and so can be used various times for launching satellites in space.
Generally, this type of launch vehicle will return back to earth after leaving the satellite in space. Sometimes it is given the name, space shuttle.
Functions of RLV are similar to the functions of first and second stages of ELV.
However, in the third stage, the satellite is inserted with a cargo bay and the satellite gets ejected from the cargo bay when the RLV attains an elevation of around 150 to 200 miles.
Once this height is achieved then the shuttle will be fired thereby placing the satellite in the transfer orbit. After this, the space shuttle will return back to earth for reuse.
Advantages and Limitations of Satellite Launch Vehicles
Advantages of Expendable Launch Vehicles:
- Simpler in design than reusable launch systems.
- Lower Development Costs.
- Low risk of mission failure.
- Short time to launch.
- Offer greater payloads.
Limitations of Expendable Launch Vehicles
- Usable only once.
- Have a significantly higher per-launch cost than modern reusable vehicles.
Advantages of Reusable Launch Vehicles:
- Lower Cost per Launch.
- Improved Environmental Footprint.
- Reduced material cost due to reusability.
- Increased Launch Flexibility.
Limitations of Reusable Launch Vehicles:
- Landing and recovery require a high degree of precision and accuracy.
- High Development Costs.
- Technical Complexity.
Also Read:
Indian Remote Sensing Satellite Program | IRS Satellite Program
GAGAN: importance of GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation