In this article you will get information about : Indian Remote Sensing Satellite Program or IRS Satellite Program. Applications of Remote Sensing.
What is Remote Sensing?
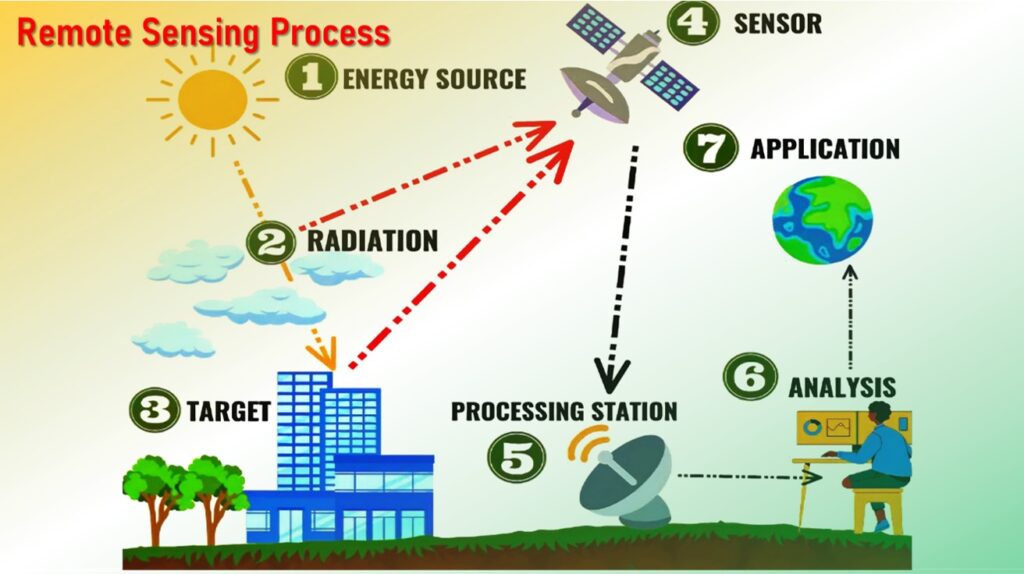
Remote sensing is the process of detecting and monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by measuring its reflected and emitted radiation energy without going physically into that particular area.
Special cameras collect remotely sensed images, which help researchers sense things about the Earth.
What is Indian Remote Sensing Satellite Program?
Following the successful demonstration flights of Bhaskara-1 and Bhaskara-2 satellites launched in 1979 and 1981, respectively, India began to develop the indigenous IRS satellite program.
The program was developed to support the national economy in the areas of agriculture, water resources, forestry and ecology, geology, watersheds, marine fisheries and coastal management.
The remote sensing programme in India under the ISRO started off in 1988 with the IRS-1A (first of the series of indigenous state-of-art operating remote sensing satellites).
Principal Capabilities IRS Satellite
The program involved the expansion of three principal capabilities:
- To design, build and launch satellites to a sun synchronous orbit.
- To establish and operate ground stations for spacecraft control, data transfer along with data processing and archival.
- To use the data obtained for various applications on the ground.
Important Indian Remote Sensing Satellites
IRS:
- IRS-1A launch in 1988
IRS-1B launch in 1991 - Importance of IRS-1A and IRS-1B: Used for remote sensing applications such as cartography, land use mapping, and forestry.
- IRS-1C launch in 1995
IRS-1D launch in 1997 - Importance of IRS-1C and IRS-1D: Had improved capabilities. Used for a wide range of
applications such as mineral exploration, coastal monitoring, and disaster management.
Resourcesat:
- Resourcesat-1 launch in 2003
Resourcesat-2 launch in 2011
Resourcesat-2A launch in 2016 - Importance of above three: Used for resource mapping and management applications such as soil moisture mapping, crop inventory, and forestry.
Cartosat:
- Cartosat 1 launch in 2005
Cartosat 2 launch in 2007
Cartosat 3 launch in 2019 - Importance of above three: Used for cartography and high-resolution imaging applications. Cartosat-3 also has an additional capability of capturing hyperspectral images.
Oceansat:
- Oceansat 1 launch in 1999
Oceansat 2 launch in 2009 - Importance of above two: Used for oceanographic applications such as sea surface temperature mapping, ocean color mapping, and ocean wind vector mapping.
RISAT:
- RISAT 1 launch in 2012
RISAT 2 launch in 2009 - Importance of above two: These satellites had synthetic aperture radar (SAR) sensors that allowed them to capture images of the earth even in cloudy or dark conditions.
Applications of Remote Sensing
- Agriculture: identifying crop conditions; determining crop type, soil moisture content and water content of the field crop; mapping of soil characteristics, soil management practices, crop production forecasting; and drought monitoring.
- Forestry: determine the forest cover and type of forest; vegetation density; control of deforestation and forest fires; and biomass estimation.
- Oceans and Coastal Monitoring: identification of ocean patterns; assessment of fish stock and marine mammal; monitoring of water quality, temperature and effects of tides and storms; mapping of coastal vegetation; and determining ocean salinity.
- Geology: bedrock and structural mapping; mineral and hydrocarbon exploration; environmental geology; sedimentation mapping and monitoring; and geo-hazard mapping.
- Hydrology: wetlands mapping and monitoring; measuring snow thickness; river and lake ice monitoring; flood mapping and monitoring; monitoring of glacier dynamics; and mapping of drainage basin.
Also Read:
Navigation with Indian Constellation (NavIC)
GAGAN: importance of GPS Aided GEO Augmented Navigation