What are Artificial Satellites?
Artificial satellites are human-built objects orbiting the Earth and other planets in the Solar System. They are used to study the Earth, other planets, aiding communication, and even to observe the distant universe. Satellites can even have people in them, like the International Space Station. The first artificial satellite was the Soviet Sputnik 1 mission, launched in 1957.
Types of Artificial Satellites
The most common types of artificial satellites based on their application are:
- Communication Satellites
- Earth observation Satellites
- Navigation Satellites
- Astronomical Satellites
Communication Satellites
What are Communication Satellites?
Communication satellites are launched to orbit around the earth or any other planet to collect information and transmit it back to the planet.
They are launched to expand the ability of networks and connections on the planet. Such a satellite can make long-distance communication and information transfer much more effortless.
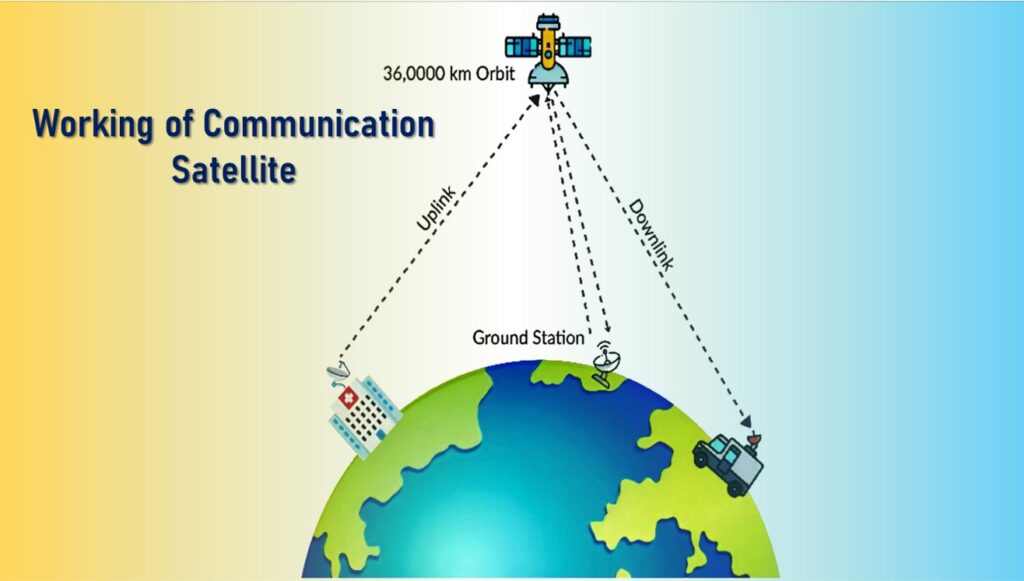
Working of Communication Satellite
- The process of communicating with satellites involves four significant steps:
- A signal transmission will occur from an Uplink Earth station or other equipment transmitting the desired signal to the satellite.
- The received signal is amplified by the satellite.
- The signal is transmitted back to the earth as a downlink.
- The antennas or receiving equipment will receive this signal.
Applications of Communication Satellites
- Telecommunication: To efficiently provide voice and data communication with the local and far-flung areas.
- Telemedicine: Mobile units are being connected seamlessly to the major hospitals and medical hubs, and medical practitioners are able to access the data rapidly.
- Tele-education: Communication satellites make education available to the students and professionals in remote locations.
- Banking: Banks and ATMs require a secured and reliable connectivity to transmit data and satellites provide that reliable connectivity for all the limitless transactions.
- Development of Internet of Things (IoT) technology through smallsats: Through the launch of small communication satellites in low earth orbits, the number of IoT devices being connected with the internet can be increased.
- Real-time tracking: To track the real-time data for earth observations such as climate change, disaster management, and also for military applications.
- TV Broadcasting: Various programs such as movies, live sports and live news are available on television through direct broadcast satellite.
- Radio Broadcast: A satellite radio provider uses satellites to broadcast audio channels of entertainment, sports, and news programs.
Earth Observation Systems
What is Earth Observation?
Earth Observation (EO) refers to the use of remote sensing technologies to monitor land, marine (seas, rivers, lakes) and atmosphere.
Earth Observation Satellites
The purpose of Earth observation type of satellites is to monitor the Earth from space and report back on any changes they observe.
The equipped sensors are different depending on the purpose such as observation of natural phenomena, disaster monitoring, changes in the Earth caused by human activity and so on.
Observation results are provided as satellite images or observation data, and can be interpreted into various information regarding the Earth.
Earth observation spacecraft can be classified as:
- Weather satellites: employed for monitoring and forecasting weather trends and providing actual weather data.
- Remote sensing satellites: its primary applications are all types of environmental monitoring and geographical mapping.
Applications of Earth Observation Satellites
- Agriculture and Soil: Information on crop statistics such as distribution and storage of food grains, government policies, pricing, procurement and food security, saline/sodic soils mapping.
- Renewable Energy: Winds, solar and wave energy resources can be assessed with the
- help of Earth observation data.
- Forest and Environment: Biodiversity characterization, wetlands, forest and biomass mapping, land degradation and desertification processes, coastal wetlands, coral reefs, mangroves, glaciers, air and water pollution assessment, etc.
- Geology, Geomorphology and Mineral Resources: Lithological, geomorphological and structural mapping, landslide hazard zonation, mineral /oil exploration, mining areas, seismotectonic studies, and geo-environmental studies.
- Land Resources: Coverage of natural resources, land use coverage, land degradation mapping, wasteland mapping, and desertification status mapping.
- Ocean Science: Identification of potential fishing zones, sea state forecasting, coastal zone studies and inputs for weather forecasting and climatic studies.
- Rural Development: Wasteland mapping/updating, watershed development and monitoring and land records modernization plan.
- Urban Development: Satellite-based remote sensing is advantageous in monitoring urban land use dynamics because of the extensive spatial coverage for mapping applications, frequent revisit periods, and wide availability.
- Water Resources: Irrigation infrastructure assessment, water resource information system, snowmelt run-off estimation, reservoir capacity evaluation and site selection for hydro-power.
- Weather and Climate: Weather satellites carry instruments called radiometers that scan the Earth to form images. Through these data, hurricanes, tornadoes, heavy rainfall, cloudy sky and even the high temperature in summer, drought, etc. can be predicted.
- Disaster Management Support: Operationally addressing various natural disasters like floods, cyclone, drought, landslide, earthquake and forest fire; research and development on early warning systems and decision support tools.
Satellite Navigation Systems
What is a Satellite Navigation System?
Satellite navigation or SatNav system is a system of artificial satellites capable of providing geo specific positioning everywhere in the world.
Satellite navigation allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location to high precision using time signals transmitted along a line of sight by radio from satellites.
Global coverage for each system is generally achieved by a satellite constellation of 18–30 medium Earth orbit (MEO) satellites spread between several orbital planes.
Types of Space Navigation System
There are two major types of space navigation systems:
- Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)
- Regional Navigation Satellite System (RNSS)
1. Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS)
The spacecraft of the Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) broadcast signals that GNSS receivers pick up and utilize for geolocation purposes, providing global coverage.
As of 2023, four global systems are operational:
- United States’ Global Positioning System (GPS) (became fully operational in 1993),
- Russia’s Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS),
- China’s BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, and
- European Union’s Galileo.
2. Regional Navigation Satellite System (RNSS)
The Regional Navigation Satellite System (RNSS) is an autonomous regional navigation system that provides coverage on a regional scale.
RNSS in operation are:
- Japan’s Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), and
- Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS) or NavIC.
Applications of Satellite Navigation
- Travel: Satellite navigation made travel to unknown places simple.
- Tracking & Monitoring: It has become common to track a package location, whether a parcel or food delivery.
- Aviation: Aircraft with SatNav services decreases the load on the pilot and decreases accidents.
- Marine: Navigation aid, self steering and automatic chart plotters technology made sailing easy.
- Surveying: Building, roads and other construction companies used SatNav technologies for precise and accurate readings.
- Mining and Archaeology: Both sectors use satnav for 3D mapping of sites for excavation and detailed site features.
- Space Applications: Spacecraft with SatNav receivers enables orbit determination precisely. It also helps in performing autonomous navigation and rendezvous tasks.
- Military Operations: Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV), missiles, and bombers are updated with guided technology that was achieved with the integration of SatNav technology.
Astronomical Satellites
What is an Astronomical Satellite?
An astronomical satellite is a giant telescope in orbit. It is able to see well without interference from the Earth’s atmosphere.
Its infrared imaging technology can function normally without being disturbed by the planet’s surface temperature.
Types of Spacecraft Used in Astronomy
Spacecraft used in astronomy can be broken down into several distinct types:
- Astronomy satellites: used to investigate different types of celestial bodies and phenomena in space.
- Climate research satellites: fitted with specific types of sensors that allows scientists to gather comprehensive, multi-faceted data on the world’s oceans and ice, land, biosphere, and atmosphere.
- Biosatellites: space-based studies on plant and animal cells and structures; plays a crucial role in the progress of medicine and biology.
Applications of Astronomical Satellites
- Make star maps and study mysterious phenomena such as black holes and quasars.
- Take pictures of the planets in the solar system.
- Make maps of different planetary surfaces.
Research Satellite: ASTROSAT
PSLV-C30 successfully launched ASTROSAT, India’s Multi Wavelength Space Observatory in lower earth orbit on September 28, 2015.
ASTROSAT is designed to observe the universe in the Visible, Ultraviolet, low and high energy X-ray regions of the electromagnetic spectrum simultaneously with the help of its five payloads.
With the success of this satellite, ISRO has proposed launching AstroSat-2 as a successor for ASTROSAT.
The observatory had a planned lifespan of five years but completed its mission in 2022.
With the successful launch of the space observatory, ASTROSAT, ISRO had put India in a select group of countries that have a space telescope to study celestial objects and processes.
Scientific Objectives of ASTROSAT
- To understand high energy processes in binary star systems containing neutron stars and black holes.
- Estimate magnetic fields of neutron stars.
- Study star birth regions and high energy processes in star systems lying beyond our galaxy.
- Detect new briefly bright X-ray sources in the sky.
- Perform a limited deep field survey of the Universe in the Ultraviolet region.
Remote Sensing satellites
What is Remote Sensing?
Remote sensing is the process of detecting and monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by measuring its reflected and emitted radiation energy without going physically into that particular area.
Special cameras collect remotely sensed images, which help researchers sense things about the Earth.
Applications of Remote Sensing
- Agriculture: identifying crop conditions; determining crop type, soil moisture content and water content of the field crop; mapping of soil characteristics, soil management practices, crop production forecasting; and drought monitoring.
- Forestry: determine the forest cover and type of forest; vegetation density; control of deforestation and forest fires; and biomass estimation.
- Oceans and Coastal Monitoring: identification of ocean patterns; assessment of fish stock and marine mammal; monitoring of water quality, temperature and effects of tides and storms; mapping of coastal vegetation; and determining ocean salinity.
- Geology: bedrock and structural mapping; mineral and hydrocarbon exploration; environmental geology; sedimentation mapping and monitoring; and geo-hazard mapping.
- Hydrology: wetlands mapping and monitoring; measuring snow thickness; river and lake ice monitoring; flood mapping and monitoring; monitoring of glacier dynamics; and mapping of drainage basin.
Also read:
Internet of Things (IoT) Device, Working and Benefits
What is Intellectual Property Rights and types of IPR?
Basic Concepts on Nanotechnology, Nanoscale, Nanomaterials, Nanoscience and Nanoengineering