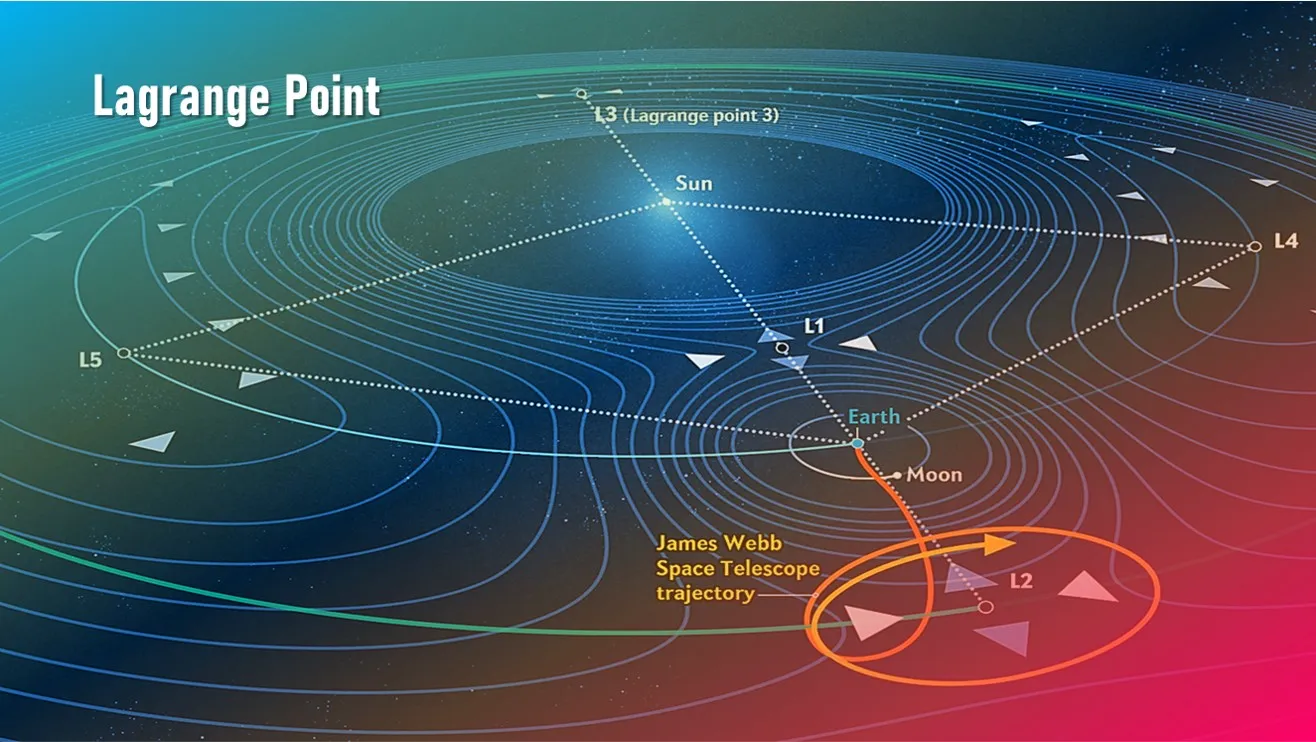
A Lagrange point is a location in space where the combined gravitational forces of two large bodies, such as Earth and the Sun or Earth and the Moon, equal the centrifugal force felt by a much smaller third body.
The interaction of the forces creates a point of equilibrium where a spacecraft may be “parked” to make observations.
These points are named after Joseph-Louis Lagrange, an 18th-century mathematician who wrote about them in a 1772 paper concerning what he called the “three-body problem.” They are also called Lagrangian points and libration points.
Different Lagrange Points
There are five special points where a small mass can orbit in a constant pattern with two larger masses. Of the five Lagrange points, three are unstable and two are stable.
The unstable Lagrange points – labelled L1, L2, and L3 – lie along the line connecting the two large masses.
The stable Lagrange points – labelled L4 and L5 – form the apex of two equilateral triangles that have the large masses at their vertices.
L1 point of the Earth-Sun system affords an uninterrupted view of the Sun, and is currently home to the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory Satellite (SOHO).
Aditya-L1 of ISRO is positioned at the L1 point.
L2 point is ideal for astronomy because a spacecraft is close enough to readily communicate with Earth, can keep Sun, Earth and Moon behind the spacecraft for solar power and provides a clear view of deep space for telescopes.
L3 lies behind the sun, opposite Earth’s orbit. For now, science has not found a use for this spot.
L4 and L5 points are home to stable orbits so long as the mass ratio between the two large masses exceeds 24.96.
- This condition is satisfied for both the Earth-Sun and Earth-Moon systems, and for many other pairs of bodies in the solar system.
FAQs related to Lagrange point
L1 Lagrange point distance from earth
The first Lagrange point i.e. L1, is 1.5 million km from the Earth towards the Sun.
How many Lagrange point exist?
There are five special points called Lagrange point, where a small mass can orbit in a constant pattern with two larger masses. From the five Lagrange points, three are unstable and two are stable.
How many stable Lagrange points are there?
There are five special points called Lagrange point. Out of five two are stable and three are unstable. The stable Lagrange points are L4 and L5.
Also Read:
8+ Applications of Space Technology in different fields
Iron Dome System and how does it works?