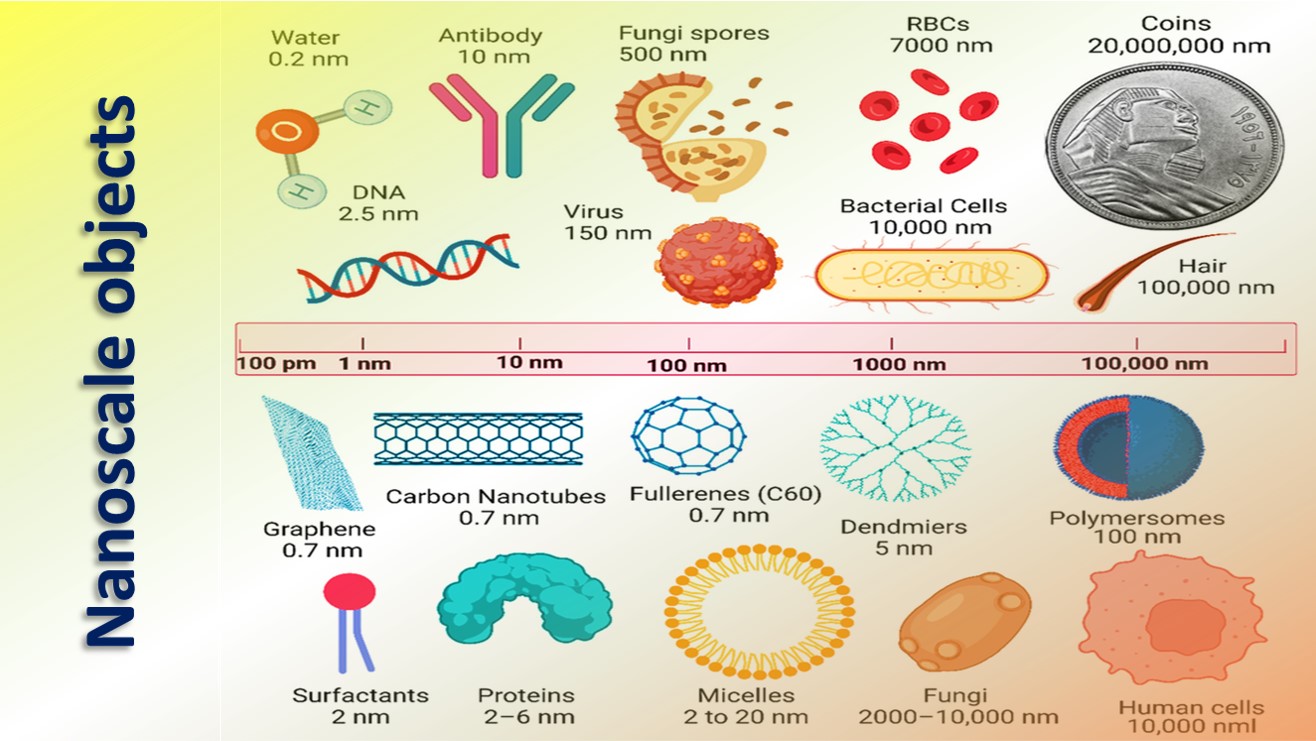
Nanoscale object deals with dimensions between approximately 1 and 100 nanometers. Larger than that is the micro-scale, and smaller than that is the atomic scale.
At the nanoscale, objects are so small that they cannot be seen even with a light microscope. Nano-scientists use tools like scanning tunneling microscopes or atomic force microscopes to observe anything at the nanoscale.
- Factors that Govern the Behaviour of Nanoscale
- How to make Nanoscale objects by using Top-down and Bottom-up Approaches
- Basic Concepts on Nanotechnology, Nanoscale, Nanomaterials, Nanoscience and Nanoengineering
- Applications of Nanomaterials in Medical and Healthcare industries
- Types of Nanomaterials and its properties in details
Factors that Govern the Behaviour of Nanoscale
Materials reduced to the nanoscale can show different properties compared to what they exhibit on a macro-scale, enabling unique applications of those materials in various unconventional ways. For instance:
- Opaque substances like copper become transparent.
- Inert materials like platinum and gold become catalysts.
- Stable materials like aluminum turn combustible.
- Solids like gold turn into liquids at room temperature.
- Insulators such as silicon become conductors.
The erratic behaviour of substances at the nanoscale is governed by two factors:
Quantum Mechanics:
When a substance is reduced to nanoscale it starts following the rules of quantum mechanics which are very different from classical physics, as a result the behaviour of substances at the nanoscale starts showing different and unique properties.
Surface to Volume Ratio:
At nanoscale the surface to volume ratio of a substance increases quite high resulting in different properties of the same material than usual. Melting points of materials can also change due to an increase in surface area at nanoscale.
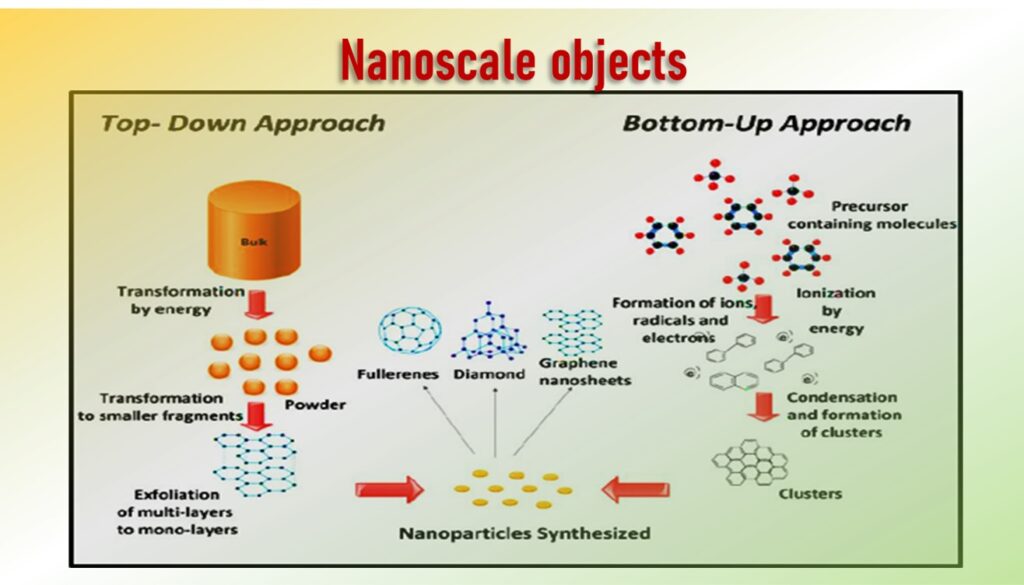
How to make Nanoscale objects by using Top-down and Bottom-up Approaches
Basically there are two ways of making nanoscale objects: top-down and bottom-up approaches.
Top-down Approach
- The top-down approach to nanotechnology involves the creation of nano-objects from a parent entity that is larger.
- This type of fabrication uses lithographic patterning techniques by which a bulk material is reduced in size to a nanoscale pattern.
- It is expensive and time-consuming for mass production but very suitable for laboratory experimentation.
Bottom-up Approach
- It is a comparatively newer approach where nanostructures can be constructed by assembly of atoms and molecules. These techniques include chemical synthesis, self-assembly and positional assembly.
- This approach will be able to produce devices in parallel and much cheaper than top-down methods, but could potentially be overwhelmed as the size and complexity of the desired assembly increases.
Also Read










4 thoughts on “What is Nanoscale objects and its Behavior”